Hello friends
With great enthusiasm, let’s explore interesting topics related to Exploring the Wonders of Marine Fish: A Guide to Diverse Species. Let’s take a good look at the following information so that our insight increases and opens our minds further.
Exploring the Wonders of Marine Fish: A Guide to Diverse Species

The world’s oceans are home to an incredible array of marine life, with over 34,000 identified species, and yet, to date, no one has explored even a fraction of the profound diversity of marine fish. From the majestic mantas to the vibrant corals, and from the swift schools of tuna to the serene sea turtles, marine fish have captivated human imagination for centuries. This article aims to delve into the world of marine fish, providing a comprehensive guide to the diverse species found in the world’s oceans.
Marine Fish: An Introduction
Marine fish are found in every ocean, from the shallowest tide pools to the deepest, darkest depths of the Mariana Trench. They come in a wide range of shapes, sizes, and colors, from the diminutive neon tetra to the enormous whale shark. Marine fish play a vital role in maintaining the balance of the marine ecosystem, serving as both predators and prey for other marine animals.
Types of Marine Fish
There are several types of marine fish, including:
- Bony Fish: These fish have a skeleton made of bone and are characterized by their ability to breathe using gills. Examples include species like the clownfish and the blue tang.
- Cartilaginous Fish: These fish have a skeleton made of cartilage and are generally more primitive than bony fish. Examples include species like the shark and the ray.
- Jawless Fish: These fish have a unique head structure without a jaw. Examples include species like the lamprey and the hagfish.
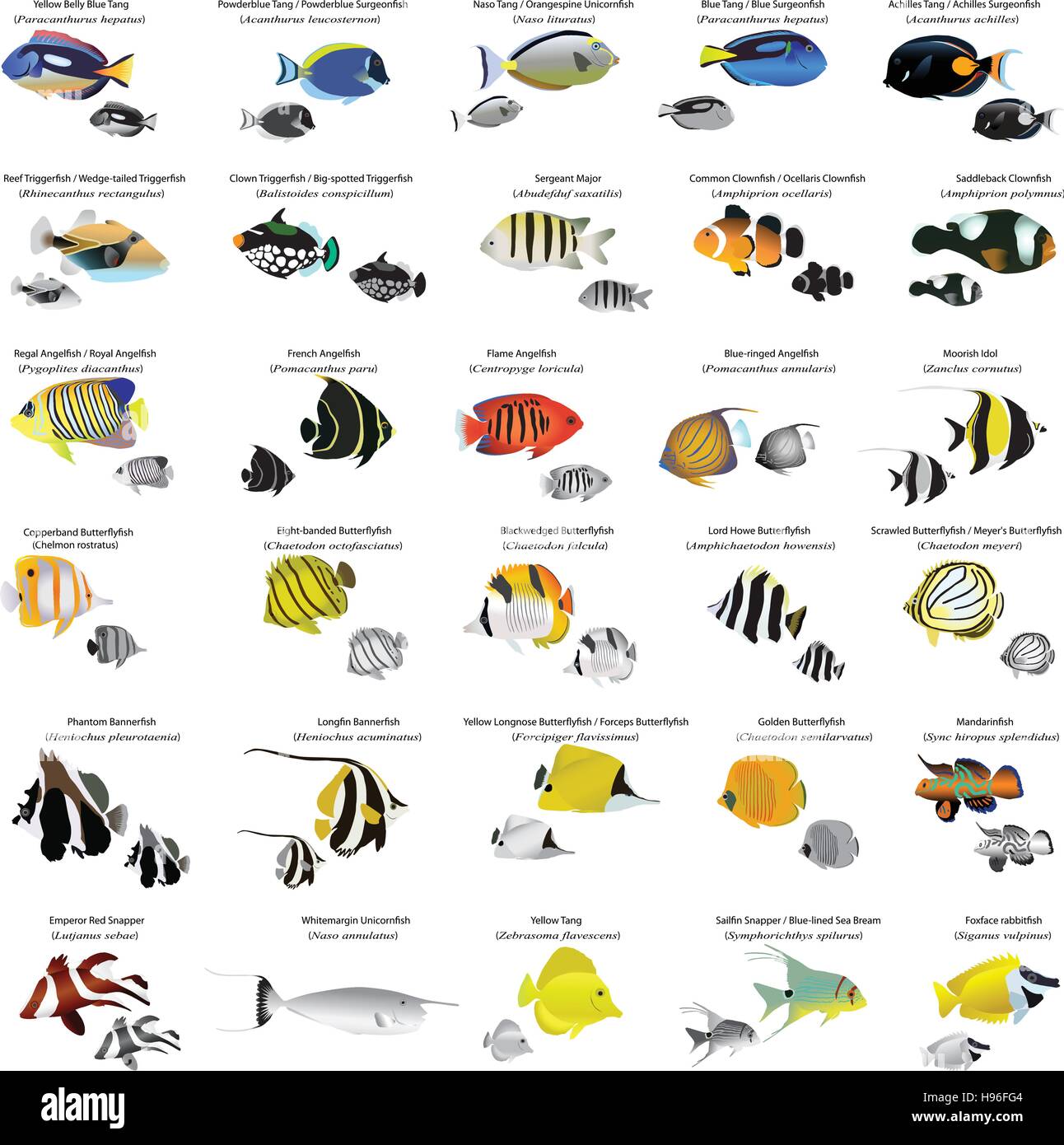
Species of Marine Fish: A Comprehensive Guide
Here, we’ll explore some of the most fascinating species of marine fish found in the world’s oceans:
- Manta Ray (Manta Birostris): The manta ray is one of the largest fish in the world, with a wingspan of up to 7 meters. These majestic creatures are filter feeders, using their wide mouths to consume vast amounts of plankton and small fish.
- Lion’s Mane Jellyfish (Cyanea Capillata): Not to be confused with the lion’s mane jellyfish, this species is actually a type of fish. The lion’s mane jellyfish is a large, bioluminescent fish found in the Indo-Pacific region, characterized by its distinctive yellow-brown color and impressive tentacles.
- Sea Dragon (Syngnathidae): The sea dragon is a type of fish in the Syngnathidae family, characterized by its elaborate appearance and habits of symbiotic relationships with corals.
- Parrotfish (Scaridae): Parrotfish are colorful fish found in tropical waters worldwide, characterized by their large, flat bodies and vibrant colors. They use their powerful teeth to crush coral and shells, helping to maintain the balance of the coral reef ecosystem.
- Butterflyfish (Chaetodontidae): Butterflyfish are small to medium-sized fish found in tropical waters worldwide, characterized by their striking colors and patterns. They use their distinctive tails to herd plankton and small fish together, creating an impressive shoal.
- Triggerfish (Balistidae): Triggerfish are small to medium-sized fish found in tropical waters worldwide, characterized by their distinctive "trigger" which they use to protect themselves from predators.
- Wrasse (Labridae): Wrasse are colorful fish found in tropical waters worldwide, characterized by their bright colors and elaborate antennae.
- Triggerfish (Boops Lineatus): The triggerfish is a small species of fish found in tropical waters worldwide, characterized by its distinctive "trigger" and vibrant colors.
Habitats and Distribution of Marine Fish
Marine fish can be found in a wide range of habitats, from shallow tide pools to the deepest, darkest depths of the ocean. Some of the most notable habitats of marine fish include:
- Coral Reefs: Coral reefs are some of the most diverse ecosystems on the planet, providing a home for a vast array of marine fish species.
- Deep-Sea Habitats: The deep sea is a mysterious and largely unexplored world, home to a vast array of marine animals, including fish.
- Mid-Water Habitats: The mid-water region is characterized by its low light levels and diverse ecosystem, providing a home for a wide range of marine fish species.
Closing
Thus, we hope this article can provide you with valuable insight into Exploring the Wonders of Marine Fish: A Guide to Diverse Species. We also thank you very much for the time you have taken to read this article. Don’t forget to visit this simple blog again to read other articles about unique, cool and extraordinary information. May you all always be given: A blessed age, Physical and spiritual health, and smooth sustenance, amen.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/coral-reef-with-turtle-georgette-douwma-getty-57c4729c5f9b5855e5bab801.jpg)